Trade and Assistance Review 2019-20
Annual report series
The Trade and Assistance Review 2019-20 was released on 14 July 2021.
The review contains the Commission’s latest quantitative estimates of Australian Government assistance to industry, and provides a summary of developments in industry assistance, trade policy and foreign investment over the past year.
Download the report
- Trade and Assistance Review 2019-20 (PDF - 1573 Kb)
- Trade and Assistance Review 2019-20 (Word - 1126 Kb)
Methodological Annex
- At a glance
- Contents
- Supporting data
Media release
Pandemic led to significant new industry assistance
Significant new emergency assistance measures — including assistance provided to industry — were rolled out in 2019-20 to help prevent job losses and maintain viable businesses during the COVID-19 pandemic.
The annual Trade and Assistance Review released by the Productivity Commission estimates that $12.1 billion in assistance was provided to businesses in 2019-20, a small increase from the previous year.
The review outlines many new measures introduced in 2019-20 in response to the pandemic, but as most of the money for these initiatives was spent in 2020-21, they will be fully reflected in next year’s review.
“A feature of the pandemic — more so than in past recessions — was the highly specific effect of restrictions on specific industries,” Productivity Commission Chair Michael Brennan said.
“Well-targeted industry assistance measures have been a valuable part of the pandemic response,” Mr Brennan said.
“As always, the art is to maintain such measures long enough to help viable businesses through the crisis, without them becoming a permanent feature,” Mr Brennan said.
2019-20 saw a continuation of the long term trend of industry assistance taking the form of budgetary outlays — such as subsidies and grants — and tax concessions, rather than tariffs.
The review also examines the range of trade measures that China has imposed on some Australian exports over the past year — including on barley, coal, wine, cotton and timber.
For some of these products — such as barley and coal — producers have rapidly expanded into other markets while, for more differentiated products such as wine, finding new markets has proved more challenging.
Notwithstanding these trade measures and their impacts on exporters, strong iron ore exports has meant that the value of goods exported to China in 2020 was similar to 2019.
Flows of foreign direct investment into Australia fell from over $56 billion in 2019 to under $30 billion in 2020 — a reflection of the dampening effect of the pandemic on investment flows globally — with Australia’s largest flows coming from Japan, the United Kingdom and Singapore.
The Trade and Assistance Review 2019-20 can be found at: www.pc.gov.au/tar2019-20
Media requests
02 6240 3330 / media@pc.gov.au
Infographic
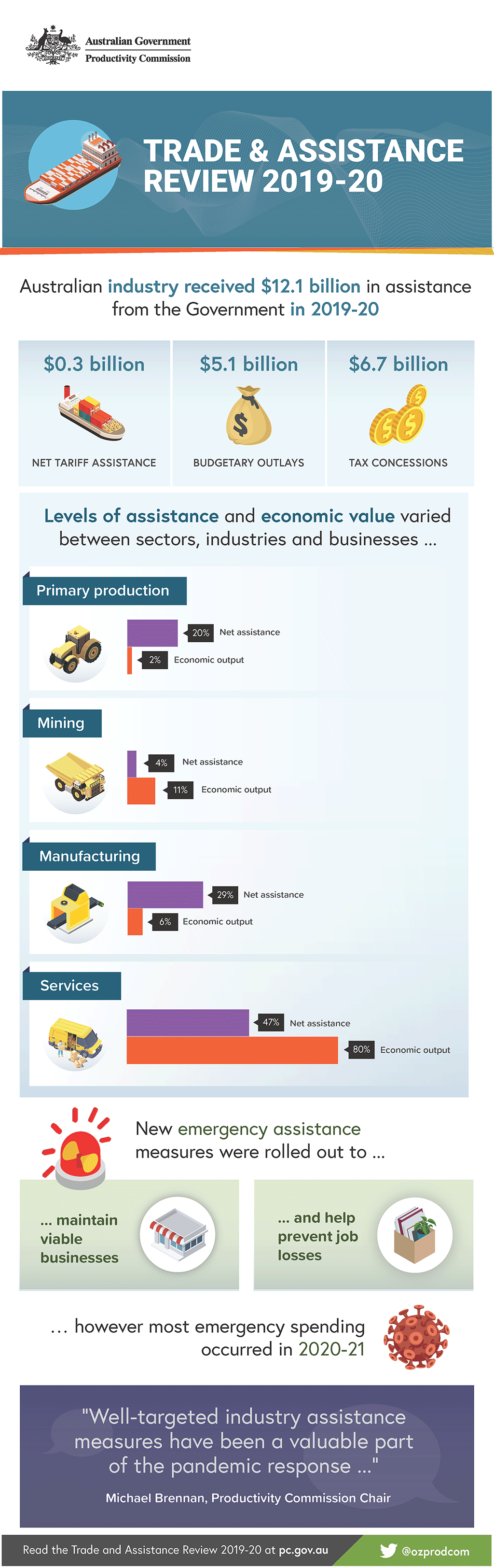
Text version of the infographic
Trade and Assistance Review 2019-20
Australian industry received $12.1 billion in assistance from the Government in 2019-20.
- Net tariff assistance $0.3 billion
- Budgetary outlays $5.1 billion
- Tax concessions $6.7 billion
Levels of assistance and economic value varied between sectors, industries and businesses.
Primary production
- Net assistance 20%
- Economic output 2%
Mining
- Net assistance 4%
- Economic output 11%
Manufacturing
- Net assistance 29%
- Economic output 6%
Services
- Net assistance 47%
- Economic output 80%
New emergency assistance measures were rolled out to maintain viable businesses and help prevent job losses.
However most emergency spending occurred in 2020-21.
"Well-targeted industry assistance measures have been a valuable part of the pandemic response"
Michael Brennan, Productivity Commission Chair
Read the Trade and Assistance Review 2019-20 at pc.gov.au
- Preliminaries: Cover, Copyright and publication detail, Foreword, Contents and, Abbreviations and explanations
- Chapter 1 Assistance estimates
- 1.1 Aggregate assistance level and rates
- 1.2 A closer look at tariff assistance
- 1.3 A closer look at budgetary assistance
- Chapter 2 Industry assistance developments
- 2.1 Assistance related to the COVID-19 pandemic
- 2.2 Other recent industry assistance
- 2.3 Some observations on recent industry assistance developments
- Chapter 3 Trade policy developments
- 3.1 How the COVID-19 pandemic has affected Australia’s trading environment
- 3.2 China imposed significant trade barriers on some Australian exports
- 3.3 Developments in multilateral and plurilateral agreements
- 3.4 Developments in bilateral and regional agreements
- 3.5 Australia’s WTO disputes
- 3.6 Anti-dumping continues to be a prominent feature of Australian trade policy
- Chapter 4 Foreign investment developments
- 4.1 A snapshot of foreign investment in and by Australia
- 4.2 Developments in foreign investment policy settings
- Appendix A How the assistance estimates are calculated
- Appendix B Assistance estimates tables (online only)
- References